As cryptocurrency prices surge, many novice investors are purchasing crypto. However, this promising opportunity is attracting not only investors but also hackers, scammers, and other nefarious actors who perceive these inexperienced investors as vulnerable targets. Although investing in crypto comes with various potential hazards, safeguarding one’s funds is unquestionably a top priority.
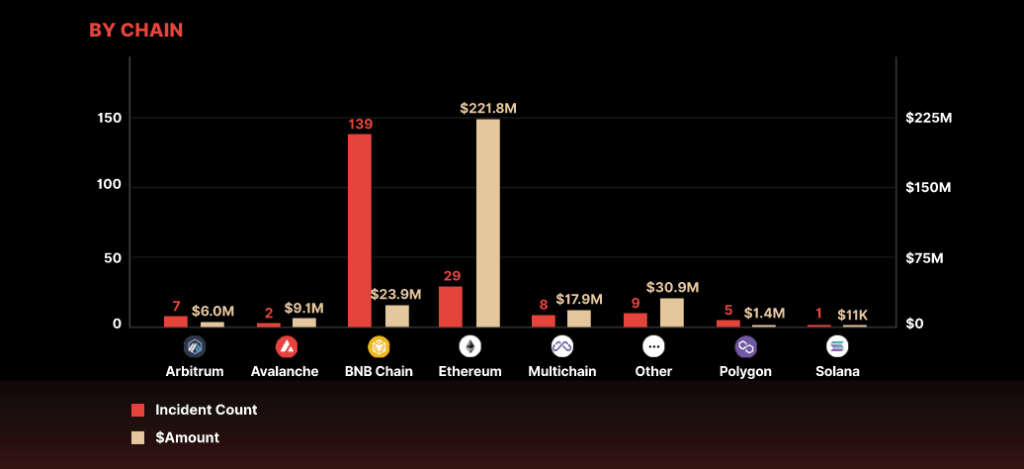
According to CertiK’s quarterly report, on-chain data has been consolidated to reveal that hackers were able to access over $320 million in the first quarter of 2023. Compared to the first and fourth quarters of 2022, where hackers stole approximately $1.3 billion and $950 million, the losses were significantly lower. Within the first quarter of 2023, 90 exit scams resulted in a loss of over $31 million, while 52 flash loan and oracle manipulation exploits accounted for more than $222 million in losses. CertiK noted that BNB Chain had the highest number of incidents, with 139 incidents recorded during the quarter.
In this article, we will outline the various methods that hackers may employ to steal your cryptocurrency and provide guidance on the measures you can take to make it highly improbable for you to become a victim of such schemes.
Let’s jump in and discuss ways to protect your crypto from digital theft.
Expect Scams
The nature of cryptocurrency, lots of crypto assets, and lack of regulations have made it a sweet spot for scammers from different backgrounds. In contrast to traditional finances, as a crypto investor, you must exercise a great deal of caution (coupled with a healthy amount of skepticism) to ensure the safety of your investments.
Here are some common cryptocurrency scams to look out for;
Phishing scams: These are fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information, such as login credentials and private keys, by posing as a trustworthy entity through emails, social media, or other communication channels.
Fake wallets and exchanges: These websites or apps appear to be legitimate crypto wallets or exchanges but are designed to steal investors’ funds or private keys.
ICO scams: Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) are similar to Initial Public Offerings (IPOs), but instead of offering shares in a company, they offer new cryptocurrencies to investors. However, some ICOs have turned out to be scams, where the organizers take investors’ money and disappear.
Giveaway Scams: Scammers may lure victims into supposedly lucrative investments by posing as an “investment fund,” “experienced manager,” “celebrity,” or “large investment firm.” The nature of these schemes may vary, with some criminals absconding with the initial payment, while others provide the victim with a modest profit to encourage further investment.
How To Protect Yourself From The Scams Listed Above
- Always double-check the validity of any firms, individuals, or websites that offer to help you invest.
- Don’t make any hasty decisions, and carefully study any new investment opportunity you encounter. Fraudsters often rush their victims into acting before they realize what’s happening.
- Ignore any unexpected offers. If you come across a crypto investment opportunity that appears to be profitable on social media, email, or instant messaging, it’s probably a scam. Rather than investigating every offer, it’s best to disregard anything you did not actively seek out.
Use Two-Factor Authentication For Your Exchange
Your cryptocurrency exchange wallet should be treated like your Bank mobile app. If a hacker gets access to the account in your wallet, they can “withdraw” your crypto to a wallet address under their own control.
One of the most effective measures to thwart these attacks is to ensure you buy your crypto through secure channels and then activate two-factor authentication (2FA) for withdrawals on your exchange application.
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security feature that provides an extra layer of protection to your crypto exchange account. When 2FA is enabled, you will need to provide a second form of authentication, usually a unique code generated by a separate authentication app or sent to your registered mobile device, in addition to your usual username and password, to complete a withdrawal request.
This added layer of security makes it much more difficult for hackers or scammers to gain unauthorized access to your account and steal your crypto assets. With 2FA enabled for withdrawals, even if someone has managed to steal your login credentials, they would still need access to your authentication app or mobile device to approve the transaction.
It’s always advisable to use 2FA for all your crypto-related accounts to increase the security of your assets and protect yourself against potential fraud or theft.
Back-Up Your Private Key Properly
Let’s say you’ve downloaded wallet software and started setting it up. You’re immediately confronted with what may be an unfamiliar experience: You’re told to back up your private key.
In cryptocurrency, a private key is a unique alphanumeric code that provides access to your digital assets, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies. The private key is a password or a digital signature that authorizes transactions and allows you to control your crypto assets.
Each private key is mathematically linked to a public key, which is used to receive funds in a cryptocurrency wallet. To conduct a transaction, the private key is required to digitally sign the transaction, which verifies that the wallet owner authorizes it.
Since private keys are essential to accessing and controlling your crypto assets, keeping them secure is crucial. Anyone with access to your private key can steal your digital assets. Therefore, storing your private keys in a secure location, such as a hardware wallet, a paper wallet, or a digital wallet that uses multi-factor authentication and other advanced security features to protect your private keys from theft or loss.
Keep the following security measures in mind:
- Back up your private key on a physical piece of paper.
- Keep the backup safe where it can’t catch fire or get water damage.
- Don’t keep plaintext copies or screenshots of your private key on your PC.
- Keep the location of your physical backup a secret.
- If your device crashes, use your private key to recover your accounts.

Use a Hardware Wallet If Possible
Using a hardware wallet is an important security measure for anyone who invests or holds cryptocurrency. A hardware wallet is a physical device that stores your private keys offline, making it nearly impossible for hackers or malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to your crypto assets.
Unlike a software wallet, which stores your private keys on your computer or mobile device, a hardware wallet keeps your private keys in a secure environment that is isolated from the internet. This means that your private keys remain secure even if malware or a virus compromises your computer or mobile device.
When you want to conduct a transaction, you simply connect your hardware wallet to your computer or mobile device and authorize the transaction by entering your PIN or other security measures. Once the transaction is complete, you can disconnect your hardware wallet, and your private keys are once again safely stored offline.
Using a hardware wallet provides an extra layer of security to your crypto assets and protects them from potential theft or loss. While you can take other security measures, such as using two-factor authentication, keeping your private keys offline is one of the most effective ways to safeguard your cryptocurrency.